| QUESTION | ANSWER | EXPLANATION |
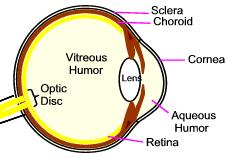
| Thin watery fluid, which is filled in the space just behind the cornea | Aqueous humor | Aqueous humor helps in maintaining pressure of the eyeball and nutrition of cornea and lens. |
Identify iris in this diagram.
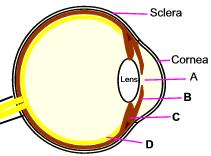
| B | Iris is a part of middle coat of the eye. It lies in front of the lens. Pigment present in the iris imparts color to the eye. |
| Coiled structure located in the inner ear is known as _______. | Cochlea | Cochlea is snail like in appearance. It has got 2 turns around the central axis. Endorgan of hearing is situated in the cochlea.
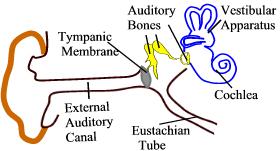 |
| Which part of the internal ear is meant for hearing? | Cochlea | Cochlea is snail like in appearance. It has got 2 turns around the central axis. Endorgan of hearing is situated in the cochlea.
 |
| Outermost coat of the eyeball consists of sclera and _______. | Cornea | Outermost coat of the eyeball is divided into 2 parts-
1. Cornea - is thin and more convex than sclera.
2. Sclera - is opaque and white in color. It's front part is covered by conjunctiva.
 |
Identify pupil in this diagram.
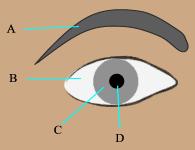 | D | Contraction and relaxation of muscles of iris results in change of pupillary size and regulates the entry of light inside the eye. |
Identify the ear ossicle B in this diagram.
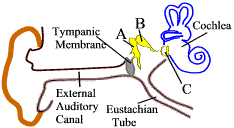 | Incus | |
| Part of the eye affected in cataract | Lens | Loss of transparency of lens or its capsule results in cataract. |
Identify the ear ossicle "A" in this diagram.
 | Malleus | Ear ossicles are responsible for conducting the sound from the ear drum to the internal ear. Malleus is one of the three ear ossicles situated in the middle ear. |
| Blind spot of the eye is also known as | Optic disc | Optic disc, found in the retina, does not contain rods and cones and is insensitive to light. That is why it is also known as blind spot.
 |
Identify the structure 'A' in this diagram.
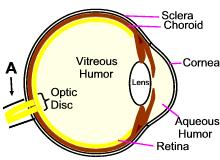 | Optic Nerve | |
| Small elevations on the tongue which contain taste buds are known as | Papillae | |
| Layer of the eye in which rods and cones are found | Retina | Rods and cones are the endorgans of vision. Rods are sensitive to dim light. Cones are sensitive to bright light and are responsible for color vision.
 |
| Smallest bone in the human body. | Stapes | Stapes is one of the three auditory bones in the human ear. It measures 2.6 to 3.4 millimetres and weighs 2 to 4 grams.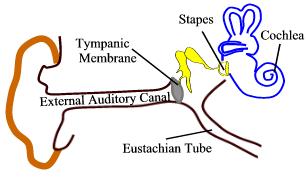 |
| The end organs (receptors) of taste sensation are called _______. | Taste buds | Taste buds are the endorgans of taste sensation. There are small projections on the tongue called papillae which contain taste buds. Nerve fibres present in the taste buds carry taste sensation to the brain. |
| _______ membrane is found between external and middle ear. | Tympanic | Tympanic membrane is a thin, shiny membrane between external auditory canal and middle ear.
 |
| _______ apparatus is a part of the internal ear and is responsible for maintenance of equilibrium and posture. | Vestibular |
 |
| Viscous fluid filled in the space behind the lens: | Vitreous humor |
 |
| True or false: The end organs (receptors) of smell are known as olfactory neurons. | True | Olfactory neurons together form the olfactory nerve which conducts information to the brain. |
| True or false: Few taste receptors are also found in the cheek. | True | |
| True or false: Choroid is the layer of the eye situated in between retina and sclera. | True | Middle coat of the eyeball is divided into 3 parts:
1.Choroid
2. Ciliary Body
3. Iris |
| True or false: Lens has the property to change its curvature. | True | Lens is a biconvex structure, covered by the lens capsule. Change in curvature of lens helps in accomodation i.e. to see distant and nearby objects clearly. |
| True or false: Cornea is a translucent membrane. | False | It is transparent. Loss of corneal transparency results in impairment of vision. |